Current detection method - Weikewei - accuracy up to 0.2%
Current detection methods: The most common methods for inducing current are resistance shunt, Hall effect, and induction.
Resistance shunt
A resistor shunt is a calibrated resistor located in the current path that generates a voltage drop proportional to the current based on the following conditions:
V=voltage drop; I=current; R=shunt resistance
The voltage drop measurement value is usually within the millivolt AC range. The output must be adjusted by a separate sensor to a process signal, such as 4-20mA or contact closure.
Unfortunately, the splitter has serious operational issues and potential safety hazards. Both sides of the shunt resistor are at the line voltage, which actually means introducing 480 VAC into the low-voltage control panel. Lack of isolation can cause serious harm to uninformed service personnel.
Since it is essentially a resistor, a shunt is generally considered the cheapest solution. Although it is actually a low-cost device, the signal conditioner must be able to withstand a voltage of 480 VAC and is very expensive. The installation and operating costs of resistive splitters further limit their use. Installing this device requires cutting off and re terminating the current carrying conductor, which is an expensive and time-consuming proposal. In addition, due to the fixed voltage drop (insertion impedance) of the shunt in the monitored circuit, it generates heat and wastes energy. This shunt is only suitable for direct current measurement and low-frequency alternating current measurement (<100 Hz).
霍爾效應電流傳感器
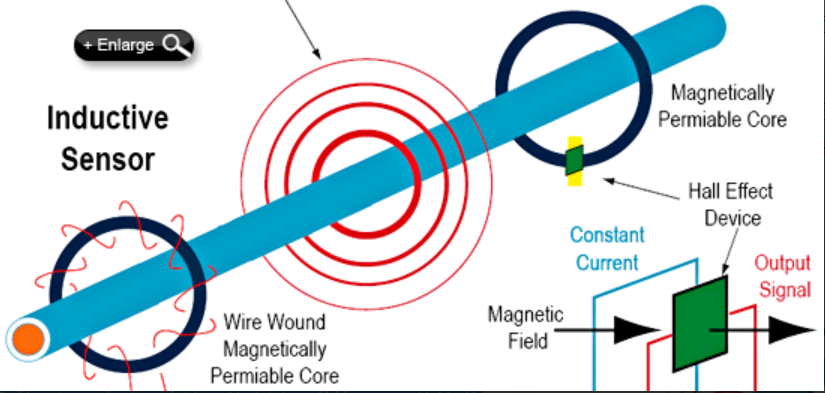
The Hall effect and induction are non-contact technologies, based on the principle that a proportional magnetic field is generated around a current carrying conductor for a given current. Both techniques can measure this magnetic field, but with different sensing methods (see Figure 1).
The Hall effect sensor consists of three basic components: the core, Hall effect devices, and signal conditioning circuits. The current conductor passes through the magnetic core, concentrating the magnetic field of the conductor. The Hall effect device is carefully installed in a small gap on the iron core, at a right angle to the concentrated magnetic field. A constant current in an airplane will excite it. When an energized Hall device is exposed to the magnetic field of the iron core, a potential difference (voltage) is generated, which can be measured and amplified into a process level signal, such as 4-20mA or contact closure.
Due to the complete isolation between the Hall sensor and the monitoring voltage, there are no safety hazards and almost no insertion impedance. It can also accurately and repetitively measure AC and DC power sources. Hall effect sensors require more energy than traditional two-wire systems powered by circuits. Subsequently, most Hall sensors are three or four wire devices.

感應式傳感器
The induction sensor consists of a winding core and a signal conditioner. The current conductor passes through a magnetic core, which amplifies the magnetic field of the conductor. AC current usually continuously changes the potential from positive to negative at a rate of 50 Hz or 60 Hz, and then back again. The expanding and contracting magnetic fields induce current in the winding. This is the principle that governs all transformers.
Current carrying conductors are usually referred to as primary, while core wire windings are referred to as secondary. The secondary current is converted into voltage and regulated to output process level signals, such as 4-20mA or contact closure. Inductive sensing can provide high precision and wide range ratio, and the output signal is inherently isolated from the monitored voltage. This isolation ensures personnel safety and generates almost imperceptible insertion loss (voltage drop) on the monitored circuit.
Inductive sensors are designed to measure AC power and typically operate in the range of 20 Hz to 100 Hz, although some units can operate in the kilohertz range. A well-designed inductive sensor can be configured as a two-wire device to reduce installation costs.